- Customer Care +91 8800900271
- About Us
- Contact Us
- Sell Your Brand
- International Orders
- Disease
- Homoeopathy
- Willmar Schwabe Germany
- SBL
- REPL
- Dr. Reckeweg
- Willmar Schwabe India
- Bakson's
- Hapdco
- Lords
- Allen
- B Jain
- Adven
- Dr. Wellmans
- Indo German
- Medisynth
- Wheezal
- Adel
- HSL
- New Life
- Bioforce
- JVS
- Hahnemann Laboratory (HL) Calcutta
- Bios Laboratory (BL)
- Parul Homoeo Laboratories (PHL)
- Allen Calcutta
- Bhandari
- Dr. Bhargava
- PHBL
- SSL
- Dr Vijay's
- Natcure
- Kent Pharmaceuticals
- Similia
- Ralson
- St. George
- SHL
- Burnette's Homoeopathy
- Purusottam Homeo Bikas Laboratory (PHBL)
- Father Muller Pharmaceuicals
- National Homoeo Laboratory
- EL Dr. Lal Singh Expertise
- Dr Patel's
- Ayurveda
- Unani
- Health & Fitness
- Books
- Veterinary
- Online Consultation
- International Orders
The Vaccine In Your Body~ Homoeopathy and Vaccinosis.
- By: Dr Plakshi Ahuja
- Profession: BHMS, DNHE, MD (Scholar)
- Category: Homoeopathy
- Apr 22, 2021
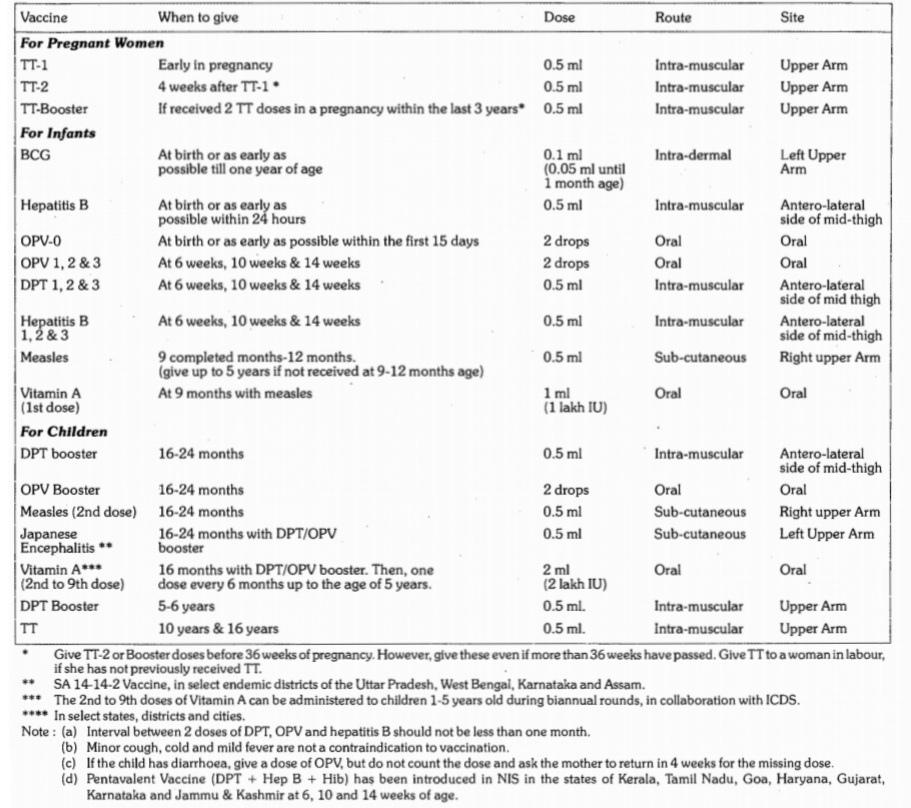
Vaccine is an immune-biological substance designed to produce specific protection against a specific disease. It stimulates the production of protective antibody and other immune mechanisms.
Over the last century, Vaccination has been the most effective medical strategy to control infectious diseases. Small pox has been eradicated world wide and poliomyelitis is almost eradicated. Vaccination is estimated to save at least 2-3 million lives.
Vaccines may be prepared from live modified organisms, inactivated or killed organisms, extracted cellular fractions, toxoids or combination of both.
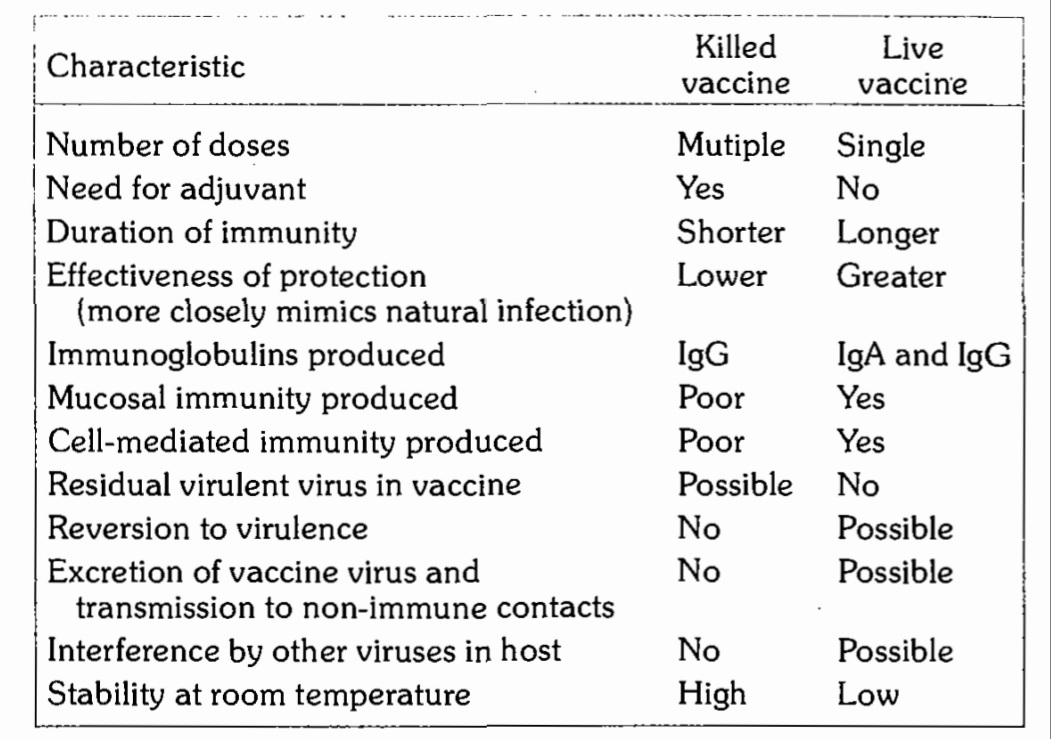
- Live Vaccines: Live Vaccines are prepared from live or wild organisms. Live vaccines should not be administerd to persons with immune deficiency diseases or to persons whose immune response may be suppressed because of leukaemia, lymphoma or malignancy or because of therapy with corticosteroids, alkylating agents, antimetabolic agents or radiations, and even in pregnancy. Vaccines like BCG, Measles, Oral Polio are Live Vaccines.
- Inacivated or killed Vaccines: Inactivated Vaccines are produced by growing virus or bacteria in culture media and then activating them with heat or chemicals, usually formaline, when injected into the body stimulate active immunity. They are usually safe but generally less effective than live vaccines.
Difference between Live and killed Vaccine
- Subunit Vaccines: A vaccine can be made of single or multiple antigenic components of a microorganism that are capable of stimulating a specific immune response sufficient to protect from the relevant pathogen infection or from the clinical manifestation of the disease.
- Combinations: If more than one kind of immunizing agent is included in the vaccine, it is called combined or mixed vaccine. The aim of the mixed vaccine is to simplify administration, reduce costs, minimize the number of contacts of patient with the health system, reducing the storage cost, improving timeline of vaccination and facilitating the addition of new vaccine into immunization programme. The common combinations are:
- DPT (Diptheria -Pertussis -Tetanus)
- DT (Diptheria-Tetanus)
- DP (Diptheria -Pertussis)
- MMR (Measles, Mumps and Rubella)
The term ‘vaccinosis’ was coined by Dr. Goullon of Weimar in a paper he published on the subject in 1877. He related it to the sycosis as described by Hahnemann and related the symptoms occurring after smallpox vaccination to the symptoms of sycotic gonorrhea.
Vaccinosis is defined as the malaise, effects or sequelae caused by the administration of vaccines to healthy individuals, including fever, muscular aches, bone pain, eruptions, ulcerations and prostration
Vaccine Reactions may be classified into
- Common, Minor Reactions
- Rare, More Serious Reactions
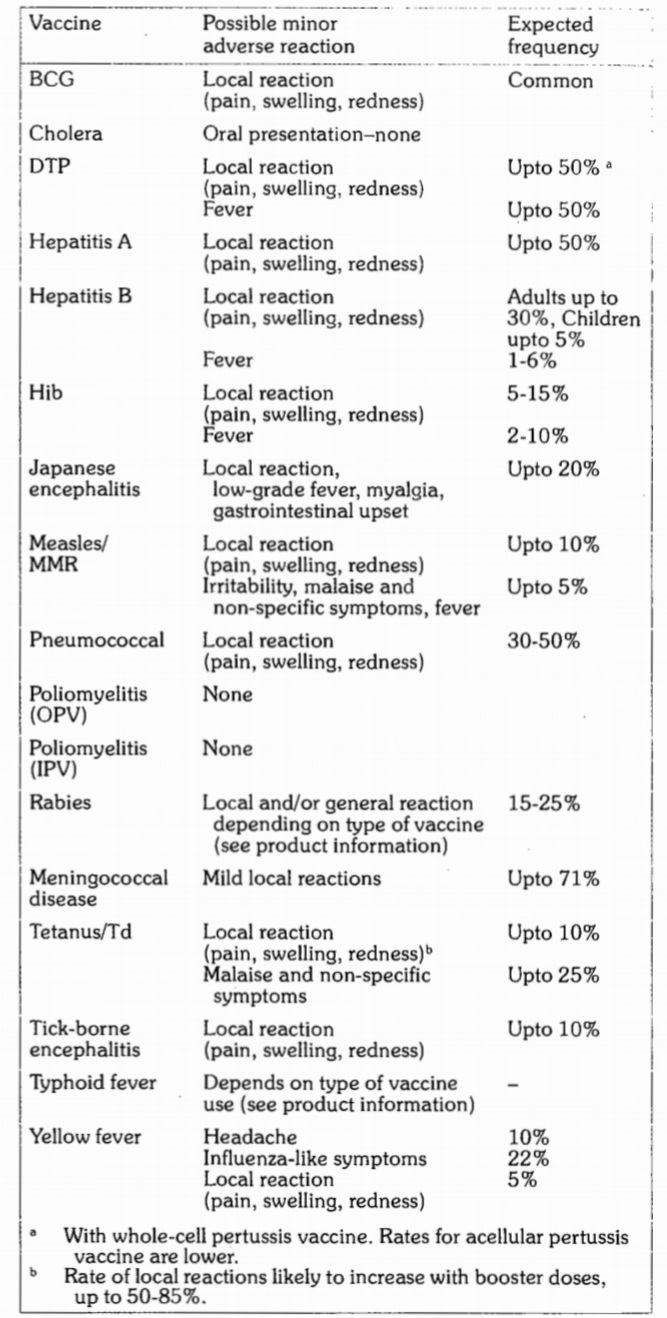
- Common, Minor Reactions: Local reactions, fever and systemic symptoms can result as a part of immune response. A successful vaccine reduces these reactions to a minimum while producing the best possible immunity.The local reactions include Pain, Swelling, Redness at the site of injection. BCG causes a specific local reaction that starts as papule, 2 or more weeks after immunization that then becomes ulcerated and heals after several months leaving a scar. Keloid (thickened scar tissue) from the BCG Lesion is more common Among Asian Countries.
The Common Minor Vaccine Reactions:
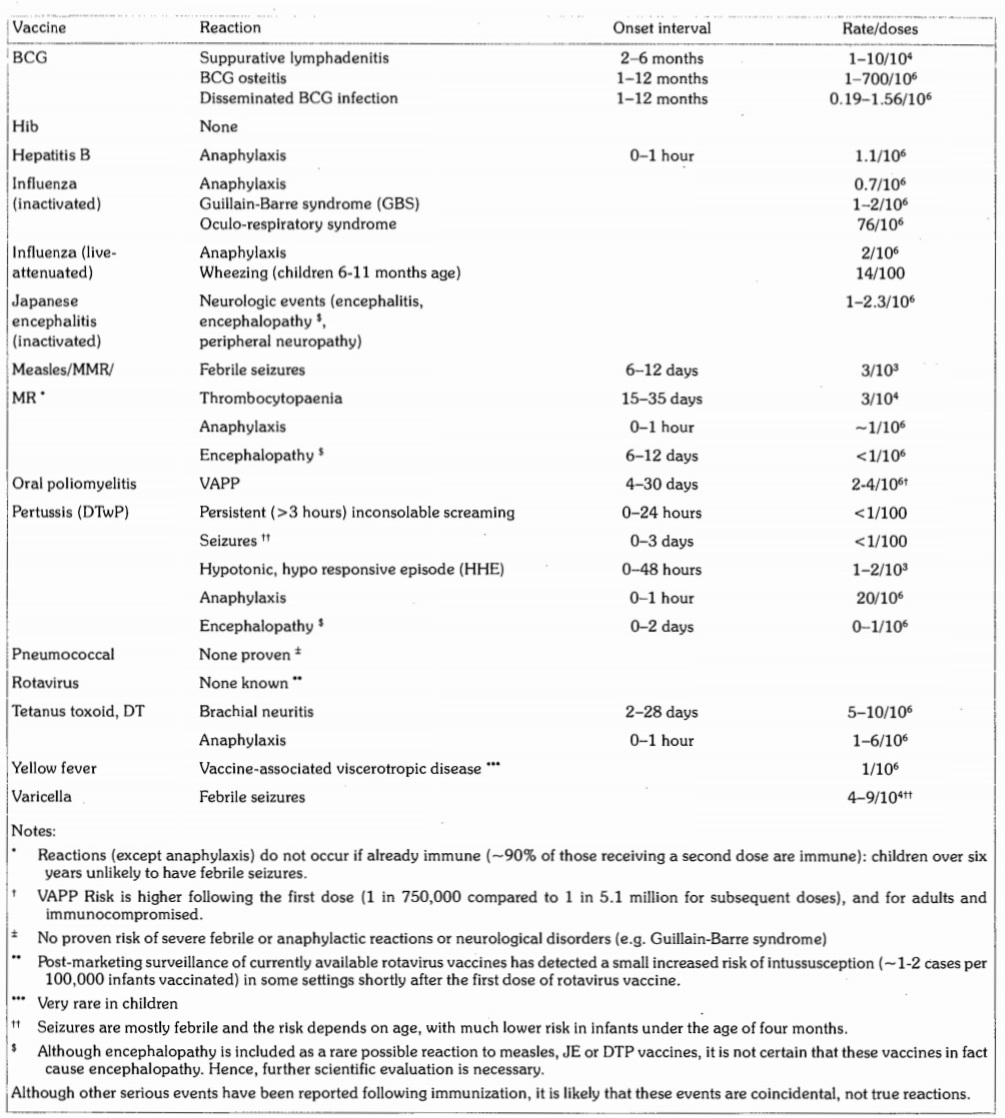
- Rare, More Serious Reactions: An Adverse event following immunization will be considered serious if it results in death, is life-threatening, requires hospitalization, results in persistent or significant disability or requires intervention to prevent permanent impairment or damage. The most rare and serious vaccine reactions include seizures, thrombocytopenia, Persistent inconsolable screaming. These reactions do not lead to long term problems.
The Rare, serious Vaccine Reactions:
Materia Medica
- Mezereum: Eczema and itching eruptions after vaccination. Eczema: intolerable itching worse in bed and from touch; copious, serous exudation. Eruptions Ulcerate and form thick scabs under which purulent matter exudes.
- Crotalus Horridus: Post vaccination eruptions. Bad effects of vaccination. Boils, Carbuncles and eruptions surrounded by purplish, mottled skin and edema. Soreness relieved by pressure.
- Silicea: Bad effects of vaccination, especially abscesses and convulsions. Checks the suppurative process. For long continuing offensive foot sweat has been suppressed by vaccination. When the vaccination lesion fails to heal and becomes a chronically discharging sore Silica may cause healing, not by suppressive action locally but because of its curative action internally. Pustular acne and other forms of pustular eruptions follow vaccination. . It will also prevent the development of an abscessed appendix following vaccination
- Thuja: It has specific antibacterial action as in gonorrhoea and vaccination. This is a great homoeopathic antidote for the evil effects often following vaccination, even where they have persisted for many years. “Never been well since I have vaccinated’. Warts following vaccination. Vaccinosis, viz., inverterable skin problems, neuralgia etc.
- Echinacea: Running sores that sometimes follow vaccination. When boils, abscesses and carbuncles follow vaccination.The patient suffers from irregular chills, fever and sweat and is weak, achy and easily fatigued. Sensation of weakness in the stomach and around the heart. Desire to lie down, and better in general from resting
- Sarsaparilla: Eruption following hot weather and vaccination. Urinary complaints after vaccination.
- Vaccinum: Symptoms like that of Hahnemann’s sycosis. Neuralgia inveterate skin eruptions, Chilliness, indigestion with great flatulent distention.
- Antim Tart: Bad effects of vaccination when Thuja failed and Silicea not indicated. Drowsiness, debility and sweat are the characteristic symptoms of the drug.
- Belladonna: Erythema, indurations and nodule formation after vaccination. High fever with convulsion, redness and hot face.
- Pyrogen: High fever of the septic type. Extremely rapid pulse. Very offensive purulent discharge for the local lesion. Offensive breath and offensive perspiration. Rosy red streaks radiating from vaccination sore.
Repertory:
1. Synthesis Repertory
- HEAD – BRAIN; complaints of – vaccination; after: Variolinum
- HEAD – INFLAMMATION – Brain – vaccination; after: Acon, Thuja
- HEAD – PAIN – vaccination; from: Thuja
- EYE – INFLAMMATION – vaccination; after: Thuja
- EAR – INFLAMMATION – Media – vaccination; after; Neuralgic: Thuja
- FACE – ERUPTIONS – acne – vaccination; from: Thuja
- STOMACH – NAUSEA – vaccination; after: Silicea
- STOMACH – PAIN – vaccination; after: Thuja
- RECTUM – DIARRHEA – vaccination; after: Thuja, Silicea, Antim Tart
- STOOL – VACCINATION; after: Thuja, Apis Mel.
- RESPIRATION –ASTHMATIC–children; in;vaccination; after: Thuja, Carcinosin
- RESPIRATION – ASTHMATIC – vaccination; after: Thuja, Carcinosin
- COUGH – VACCINATION; after: Thuja, Carcinosin, Silicea, Antim Tart
- EXTREMITIES – EMACIATION – Upper limbs – vaccination; after: Thuja, Malandrinum.
- EXTREMITIES – ERUPTIONS – Legs – pustules – vaccination; after: Sulphur
- EXTREMITIES – FELON – Nail; beginning in – runaround – vaccination; after: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – FELON – Root of nail; at – vaccinations; from: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – PARALYSIS – Lower limbs – vaccination; after: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – SUPPURATION – Fingers – Nails – vaccination; after: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – Shoulders – vaccination; after: Thuja, Apis Mel.
- EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – Upper arms – vaccination: Thuja, Silicea, Sulphur.
- SLEEP – RESTLESS – vaccination; after: Thuja
- SLEEP – SLEEPLESSNESS – vaccination; after: Thuja, Mezerium, Carcinosin
- DREAMS – QUARRELS – vaccinations: Lavandula angustifolia
- DREAMS – VACCINATIONS – arguing about vaccinations: Lavandula angustifolia
- FEVER – VACCINATION; after: Carcinosin
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – boils – vaccinations; from: Thuja, Silicea
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – eczema – discharging – vaccination; after: Malandrinum
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – eczema – vaccination; from: Thuja, Mezerium, Skookum Chuck aqua, Vaccinum
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – urticaria – vaccination; from: Skookum Chuck aqua
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – vaccination; after: Thuja, Mezerium, Sarsaparilla
- SKIN – VACCINATION; after: Thuja
- GENERALS– VACCINATION; ailments after: Thuja, Mezerium, Sarsaparilla, Malandrinum, Lyssinum, Silicea, Sulphur, Vaccinum, Zincum Met.
- GENERALS – CONVULSIONS – vaccination; after: Thuja, Silicea, Carcinosin, Causticum, Cicuta, Thuja, Variolinum
- GENERALS – DEVELOPMENT – arrested – vaccinations; from: Thuja
- GENERALS – FAMILY HISTORY of – vaccination; repeated: Thuja, Siicea, Medorrhinum, Graphites, Baryta Carb
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after- never well since: Thuja, Siicea, Carcinosin, Pyrogenium
- GENERALS – PAIN – vaccination; after; neuralgic: Thuja
- GENERALS – PARALYSIS – paraplegia – vaccination; after: Arsenicum Album
- GENERALS – SEPTICEMIA, blood poisoning – smallpox vaccination; after: Malandrinum, Sarsaparilla
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after; Allergies; for: Thuja
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after – DPT; for : Silicea
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after; Childern; in: Carcinosin
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after; reaction; severe: Carcinosin
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after; never well since: Thuja, Silicea, Carcinosin, Pyrogen
- GENERALS – VACCINATION; ailments after – respond to vaccination; failure to: Thuja
2. Complete Repertory
- MIND – ANXIETY – vaccination, after: Thuja
- HEAD – PAIN – vaccination, from: Thuja, Apis
- EYES – INFLAMMATION – vaccination, after: Thuja
- STOMACH – NA– USEA – vaccination, after: Silicea
- STOMACH – PAIN – vaccination, after: Thuja
- RECTUM – DIARRHEA – general – vaccination, after: Thuja, Silicea, Antim Tart, Apis, Arsenic Alb, Sulphur
- RESPIRATION – ASTHMATIC – children – vaccination, after: Thuja, Cuprum Metallicum, Carcinosin
- RESPIRATION – ASTHMATIC – vaccination, after: Thuja, Cuprum Metallicum, Carcinosin
- CHEST – CANCER – mammae – vaccinosis: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – EMACIATION – upper limbs – vaccination, after: Plumbum Met
- EXTREMITIES – FELON, onychia, paronychia – general – run-around – vaccination, after: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – PARALYSIS – general – lower limbs – vaccination, after: Thuja
- EXTREMITIES – SWELLING – general – upper limbs – shoulders – vaccination, after: Thuja, Apis Mel.
- SLEEP – RESTLESS – vaccination, after: Thuja, Silicea, Sulphur
- SLEEP – SLEEPLESSNESS – general – vaccination, after: Thuja, Mezerium
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – vaccination, after: Thuja, Crotalus Hor, Sarsaparilla, Silicea, Mezerium, Ammonium Carb, Kali Mur
- SKIN – ERUPTIONS – eczema – vaccination, after: Thuja, Silicea, Mezerium, Ammonium Carb, Kali Mur
- GENERALITIES – CONVULSIONS, spasms – vaccination, after: Thuja, Silicea
Get the Latest Updates Blog
 Click here to Pay
Click here to Pay

Please send the screenshot at 880 090 0271

