- Customer Care +91 8800900271
- About Us
- Contact Us
- Sell Your Brand
- International Orders
- Disease
- Homoeopathy
- Willmar Schwabe Germany
- SBL
- REPL
- Dr. Reckeweg
- Willmar Schwabe India
- Bakson's
- Hapdco
- Lords
- Allen
- B Jain
- Adven
- Dr. Wellmans
- Indo German
- Medisynth
- Wheezal
- Adel
- HSL
- New Life
- Bioforce
- JVS
- Hahnemann Laboratory (HL) Calcutta
- Bios Laboratory (BL)
- Parul Homoeo Laboratories (PHL)
- Allen Calcutta
- Bhandari
- Dr. Bhargava
- PHBL
- SSL
- Dr Vijay's
- Natcure
- Kent Pharmaceuticals
- Similia
- Ralson
- St. George
- SHL
- Burnette's Homoeopathy
- Purusottam Homeo Bikas Laboratory (PHBL)
- Father Muller Pharmaceuicals
- National Homoeo Laboratory
- EL Dr. Lal Singh Expertise
- Dr Patel's
- Bangalore Bio-Plasgens (BBP)
- Boericke Research Laboratory (BRL)
- Ayurveda
- Unani
- Health & Fitness
- Books
- Veterinary
- Online Consultation
- International Orders
Login Account
Throw Your KIDNEY STONES Out Of You With Homoeopathy !
- By: Dr Plakshi Ahuja
- Profession: BHMS, DNHE, MD (Scholar)
- Category: Homoeopathy
- Nov 30, 2021
Renal calculus is a stone like body composed of urinary salts bound together by a colloid matrix of organic materials.
AETIOLOGY:
- Hyper excretion of relatively insoluble urinary constituents.
- Physical changes in urine.
- Altered urinary crystalloids and colloids.
- Decreased urinary output of citrate.
- Vitamin A deficiency.
- Prolonged immobilisation.
- Renal infection.
- Parathyroid Tumour
- Inadequate urinary drainage and urinary stasis.
- Excessive intake of animal protein, diet high in red meat, hypercalciuria, hyperoxaluria
RISK FACTORS:
- Family or personal history. If someone in your blood relation has had kidney stones then you're more likely to develop stones. If you already had one or more kidney stones, you're at increased risk of developing another.
- Dehydration. Not drinking enough water each day can increase your risk of kidney stones.
- Certain diets. Eating a diet that's high in protein, sodium (salt) and sugar may increase the risk of developing some types of kidney stones. Too much salt in diet increases the amount of calcium which the kidneys must filter and significantly increases risk of kidney stones.
- Obesity. High body mass index (BMI), large waist size and weight gain have been linked to an increased risk of kidney stones.
- Digestive diseases and surgery. Gastric bypass surgery, inflammatory bowel disease or chronic diarrhoea can cause changes in the digestive process that affect your absorption of calcium and water, increasing the amounts of stone-forming substances in urine.
- Other medical conditions such as renal tubular acidosis, cystinuria, hyperparathyroidism and repeated urinary tract infections also can increase risk of kidney stones.
- Certain supplements and medications, such as vitamin C, dietary supplements, laxatives (when used excessively), calcium-based antacids, and certain medications used to treat migraines or depression, can increase risk of kidney stones.
TYPES OF RENAL CALCULI:
- Primary stones: Stones which form apart from the gross infection in the renal pelvis and sometimes in the bladder
- Oxalate calculus (calcium oxalate): Most kidney stones are calcium stones. These are extremely hard, not so clearly defined. Foods that contain large amounts of oxalates are cabbage, rhubarb, spinach, tomato, cherry, cocao.These calculi are very hard and there hard and rough surface induce bleeding when in impact through a narrow passage.
- Uric acid and Urate calculi: They are small and hard, oval and round, yellowish or reddish brown, rough or smooth. They are multiple and occur in acid urine.Many patients with gout form uric acid stone, but gout is not a necessary condition for its formation. Uric acid stones can form in people who lose too much fluid because of chronic diarrhea or malabsorption, those who eat a Protein rich diet, and those with diabetes or metabolic syndrome. Certain genetic factors may increase risk of uric acid stones.
- Cystine calculi: They are yellow or yellowish green in colour, granular or smooth bearing a waxy appearance , soft or firm in consistency. They are usually multiple and bilateral and enlarge rapidly. These stones form in people with a hereditary disorder called cystinuria that causes the kidneys to excrete too much of a specific amino acid.
- Xanthine calculi: Rare stones, yellowish brown in colour and smooth and hard in consistency.
- Indigo calculi: Rare stones, Blue in colour.
- Matrix Calculi: Yellowish white to light tan in colour with viscid putty consistency. It is made of 65% of matrix and some calcium salts as well.
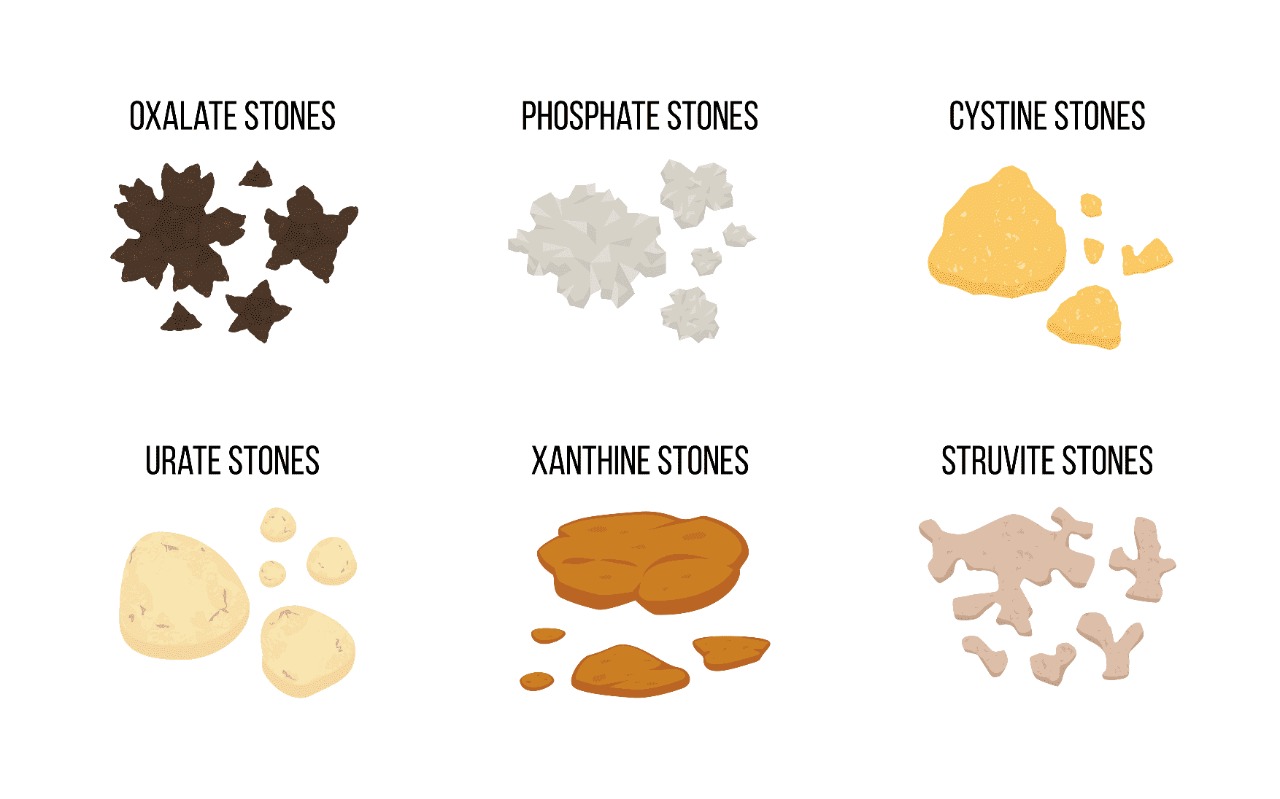

- Secondary stones: Stones which form due to infection in the bladder and sometimes in the Pelvis
- Phosphate calculi: This type of stone happens more often in people with metabolic conditions, like renal tubular acidosis (the kidneys aren’t able to help maintain proper acid balance in blood) or with people who take medications for migraines or seizures.
CLINICAL FEATURES:
- Renal pain: Dull aching to pricking type of pain in the side and back, below the ribs. Pain that radiates to the lower abdomen and groin which aggravates on exercise, manual labour and physical activities.
- Ureteric colic: When the stones is impacted in the pelviureteric junction or anywhere in the ureter.
- Recurrent UTI: Fever with chills and rigors, burning micturition, pyuria may occur, along with increased frequency of micturition.
- Hydronephrosis: Sometimes patient complains of lump in the loin and a dull ache, which are due to hydronephrosis caused by renal stone.
- Passing only small amounts of urine
- Pink, red, or brown blood in urine (hematuria)
- Small stones in urine
- Cloudy or bad-smelling urine
- Pain that comes in waves and fluctuates in intensity
- Pain during and after urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Constant need to urinate.
- Fever and chills if an infection is present
PHYSICAL SIGNS:
- Tenderness: Mostly present in the “renal angle” posteriorly.
- Muscle rigidity: Over the kidney may be found.
- Swelling: May be felt in the flank. Abdominal distension and diminished in peristalsis may accompany with ureteric colic.
DIAGNOSIS:
- Xray of kidney, bladder and ureter
- Ultra-sonography (for radio opaque stonesi.e the stones that are not visisble on Xray)
- Blood tests for kidney: Urea creatinine, BUN
GENERAL MANAGEMENT:

- Excessive amounts of milk products, strawberries, plums, spinach and asparagus should be avoided
- Large quantities of water should be taken
- There should be regular motion of bowel daily
- Exercise must be done regularly
- Balanced intake of Calcium
- Processed, Canned food should be avoided
- Sodas and sugar rich diet should be avoided
- Water in which the kidney Beans are boiled can be consumed as it helps in passage of kidney stones
- The DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet is recommended for many health problems including renal stones. It includes rich vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and low-fat dairy. It helps to limit the intake of sodium, sugar, and red meat.
- Increase the intake of magnesium from food sources like almonds, cashews, dry roasted, cereal, shredded wheat, soymilk, plain or vanilla, black beans.
HOMOEOPATHIC MEDICINES:
- Berberis Vulgaris: Top remedy for kidney stones especially in the left side. There is acute pain in the region of kidney with frequent desire to pass urine. urine contains mucus with sediments. Bubbling sensation in kidneys.
- Calcarea Carb: When there is difficulty and pain on passing the stone.
- Hydrangea: For gravel and breaking the stones and enalbling there easy passage. After expulsion of stones, it prevents there recurrence. White deposits or yellow sand in urine.
- Ocimum Can: Renal calculi in the right kidney with pain in right side. Urine smells like a musk and when allowed to stand for a while, brick dust red or yellow sediment settles at the bottom. In men, pain may also be felt in glans penis while urinating.
- Pareira Brava: Stone in the kidney for a long time and is difficult to expel it.
- Staphysagria: When urethra has been scratched from stone in bladder
- Urtica Urens: Helps in expulsion of very old kidney stones. It acts as a cleansing agent of kidneys.
- Versicaria: General dropsy due to ceasation of function of kidney to secrete urine. It helps in the secretion of urine and removes the swelling of hands, feet
- Cantharis: kidney stone where there is intense burning on passing urine. The burning may also be present before urine is passed and may continue after urination.
Subscribe Now
Get the Latest Updates Blog
 Click here to Pay
Click here to Pay

Please send the screenshot at 880 090 0271

